Superbird C2 at 144.0°E Satellite General Data, Spot Beams of the satellite with EIRP Beams corresponding to Antenna diameters, and description of the satellite.
General data
Satellite Name: Superbird C2 (Superbird 7)
Status: Active
Position: 144° E (144° E)
NORAD: 33274
Cospar ID: 2008-038A
Official Website: Click on the Spot Beam images to visit the official website
Launch date: 14-Aug-2008
About: Scroll to the bottom of the page for more satellite insights
Launch vehicle: Ariane 5 ECA
Launch mass (kg): 4820
Dry mass (kg): 2018
Manufacturer: Mitsubishi Electric Corp. (MELCO)
Model of the Satellite (bus): DS2000
Orbit: GEO
Expected lifetime: 15+ yrs.
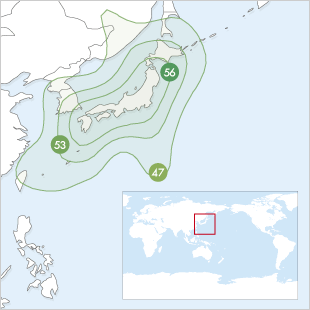
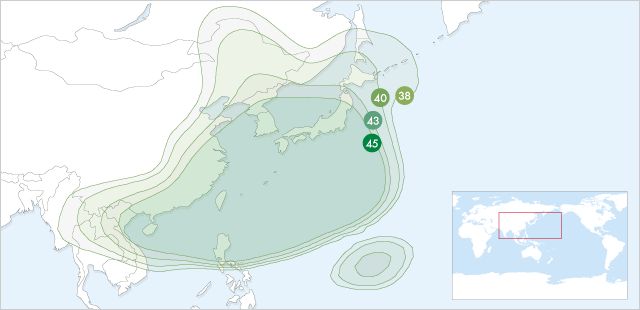
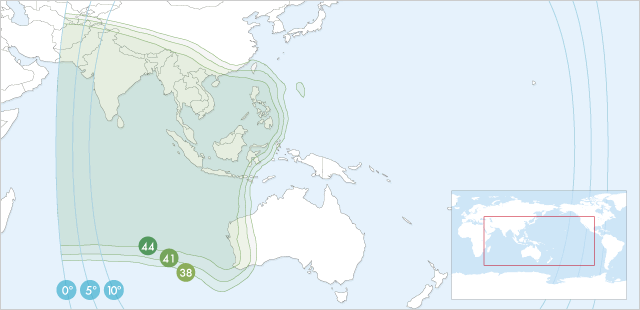
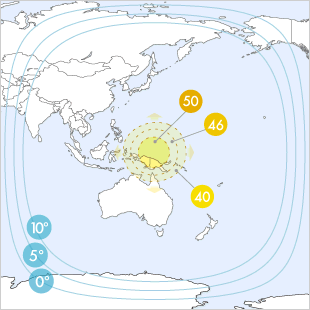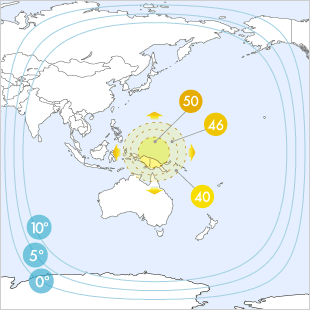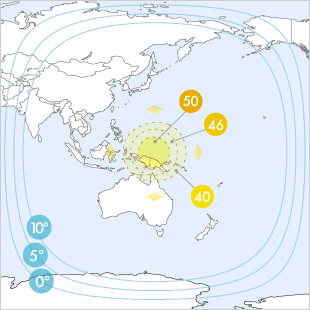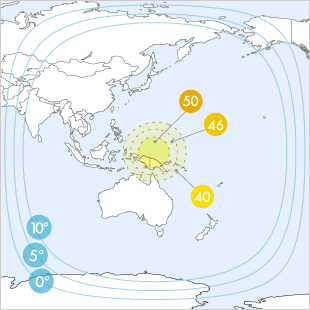
Spot Beams
| C Band | ||||||||||||
| 42 dBW | 41 dBW | 40 dBW | 39 dBW | 38 dBW | 37 dBW | 36 dBW | 35 dBW | 34 dBW | 33 dBW | 32 dBW | 31 dBW | 30 dBW |
| 80-100 cm | 90-115 cm | 100-125 cm | 115-145 cm | 125-160 cm | 145-180 cm | 160-200 cm | 180-225 cm | 200-255 cm | 225-285 cm | 255-320 cm | 285-360 cm | 320-400 cm |
| Ku Band | ||||||||||||
| 50 dBW | 49 dBW | 48 dBW | 47 dBW | 46 dBW | 45 dBW | 44 dBW | 43 dBW | 42 dBW | 41 dBW | 40 dBW | 39 dBW | 38 dBW |
| 50-60 cm | 55-65 cm | 60-75 cm | 65-85 cm | 75-95 cm | 85-105 cm | 95-120 cm | 105-135 cm | 120-150 cm | 135-170 cm | 150-190 cm | 170-215 cm | 190-240 cm |
-Watch all sports video news and highlights
-More content on social media
About
The Superbird C2 satellite, a significant player in global communications, was launched with the mission of enhancing telecommunication capabilities across the Asia-Pacific region. This satellite, developed and deployed by Space Communications Corporation (SCC), now SKY Perfect JSAT Corporation, represents an advancement in satellite technology. Positioned at a geostationary orbit of 144.0°E, the Superbird C2 maintains a fixed position relative to the Earth’s surface, ensuring consistent and reliable coverage for its designated area.
Launched in 2008, Superbird C2 was part of a broader initiative to bolster communication infrastructure, providing a wide array of services including broadcasting, data relay, and emergency communication support. The geostationary position at 144.0°E is strategically significant, as it allows the satellite to cover a vast expanse, including parts of East Asia, South Asia, and Oceania. This position maximizes the satellite’s ability to deliver high-quality, uninterrupted services to a diverse array of users, from individual consumers to large corporations and governmental bodies.
The development of Superbird C2 involved collaboration between key industry players, including satellite manufacturers and launch service providers. The satellite’s technical specifications reflect a high degree of sophistication, featuring transponders that operate in the Ku-band frequency. This enables it to support a wide range of communication services, from direct-to-home (DTH) television broadcasting to high-speed data transmission. The satellite’s design also includes redundancy systems to ensure operational reliability and longevity.
In the broader context of global communications, Superbird C2’s position at 144.0°E underscores the strategic planning inherent in satellite deployment. By occupying this orbital slot, the satellite is able to mitigate coverage overlaps and interference with other satellites, thus optimizing its service delivery. As the demand for satellite-based communication services continues to grow, the role of satellites like Superbird C2 becomes increasingly critical in maintaining and enhancing global connectivity.
Technical Specifications of Superbird C2
Superbird C2 is a geostationary communication satellite, 144.0°E position, which provides extensive data transmission services across Asia and the Pacific region. This satellite, operated by SKY Perfect JSAT Corporation, features a robust array of technical specifications that underscore its advanced communication capabilities.
The Superbird C2 satellite has a mass of approximately 4,800 kilograms at launch. Its dimensions are optimized for the spacecraft’s functionalities, with a length of about 5 meters, a width of 2.2 meters, and a height of 2.8 meters when stowed. Once deployed in orbit, the satellite’s solar arrays extend to provide a wingspan of around 24 meters. These solar arrays are crucial, as they generate the necessary power supply of approximately 7.5 kilowatts, ensuring the satellite’s systems remain operational throughout its mission life.
Transponders
Equipped with a suite of transponders, the Superbird C2 operates across multiple frequency bands. Notably, it utilizes the C-band and Ku-band frequencies, which are essential for a variety of communication services including broadcasting, telecommunications, and data relay. The C-band transponders offer stable and reliable communication links, particularly resilient to rain fade, whereas the Ku-band transponders provide higher bandwidth, catering to high-speed data transmission needs.
The satellite’s communication payload includes state-of-the-art antennas designed to enhance signal reception and transmission. This includes both fixed and steerable antennas, allowing for flexible coverage and precise targeting of service areas. Furthermore, the onboard technologies are complemented by advanced digital signal processors that optimize data handling and enhance overall performance.
One of the unique features of the Superbird C2 is its ability to support both wide and spot beam coverage, which enhances its versatility in providing tailored communication solutions. Its data transmission capabilities are formidable, with high throughput capacity ensuring efficient handling of large volumes of data.
The Superbird C2 satellite is designed with a mission lifespan of approximately 15 years. As with many geostationary satellites, plans for upgrades or replacements are typically mapped out well in advance to ensure continuity of service. SKY Perfect JSAT Corporation continues to evaluate technological advancements to determine the optimal timing for such upgrades, ensuring their satellite fleet remains at the forefront of communication technology.
Applications and Services Provided by Superbird C2
The Superbird C2 satellite, positioned at 144.0°E, serves a multitude of applications that extend across various sectors and industries. One of its primary functions is to facilitate broadcasting services. With its advanced transponder technology, Superbird C2 ensures seamless transmission of television and radio signals, reaching millions of viewers and listeners across vast geographical regions. This capability is particularly crucial for media companies that require reliable satellite broadcasting to maintain uninterrupted service.
Another significant application of Superbird C2 is in providing internet connectivity. By leveraging its high-bandwidth capabilities, the satellite supports broadband internet services, especially in remote and underserved areas where traditional terrestrial infrastructure is lacking. This has proven invaluable for businesses and communities in rural locations, enabling them to access critical online resources and participate in the digital economy.
Telecommunication Services
In the realm of telecommunications, Superbird C2 offers robust telecommunication services that include voice, data, and video communication. These services are essential for both commercial enterprises and governmental agencies that demand secure and reliable communication channels. The satellite’s ability to handle high-volume data traffic makes it a vital asset for telecommunication providers aiming to expand their coverage and improve service quality.
Superbird C2 also plays a pivotal role in data relay operations, supporting various commercial and governmental applications. For instance, it assists in maritime and aviation sectors by providing real-time communication and data exchange, which is crucial for navigation, safety, and operational efficiency. In the field of remote sensing, the satellite aids in the collection and transmission of environmental data, which is used for monitoring weather patterns, natural disasters, and other critical phenomena.
Real-world examples highlight the satellite’s impact and effectiveness. For instance, in the media industry, a leading broadcasting company relies on Superbird C2 for distributing high-definition television content to viewers across Asia-Pacific. In the maritime sector, a global shipping firm utilizes the satellite’s connectivity services to enhance onboard communication systems, ensuring smooth and efficient operations even in the most remote oceanic regions.
Overall, the diverse applications and services provided by Superbird C2 demonstrate its integral role in modern communication, connectivity, and data relay operations, benefiting a wide array of industries and sectors.
Future Challenges for Superbird C2
As we look ahead to the future of Superbird C2, several key factors and emerging trends in satellite technology are poised to shape its trajectory. One of the primary opportunities lies in advancements in satellite propulsion systems. Enhanced propulsion could significantly extend the operational life of Superbird C2, allowing it to remain in service well beyond its original lifespan. These advancements not only promise greater longevity but also improve the satellite’s maneuverability, enabling it to maintain optimal positioning with greater precision.
Another area of potential development is in satellite communication technologies. Innovations in signal processing and data transmission can boost the bandwidth and reliability of Superbird C2, making it a more robust option for a variety of applications. Emerging technologies such as high-throughput satellites (HTS) could also be integrated to enhance its performance, providing higher data rates and better quality of service to end-users.
However, the future is not without its challenges. One of the most pressing issues is the increasing amount of space debris. The proliferation of defunct satellites and other debris in Earth’s orbit poses a significant risk to operational satellites like Superbird C2. Collisions with debris can lead to catastrophic failures, necessitating the development of more sophisticated debris tracking and collision avoidance systems.
Orbital Congestion
Orbital congestion is another critical challenge. With the growing number of satellites being launched, finding and maintaining optimal orbital slots is becoming increasingly competitive. This congestion can lead to signal interference and limited space for new satellites, complicating the operational environment for Superbird C2 and its contemporaries.
Competition from other satellites is also intensifying. As new players enter the satellite communications market, Superbird C2 must continuously evolve to maintain its competitive edge. This includes adopting new technologies, improving service offerings, and exploring innovative business models to remain relevant.
Industry experts predict that the satellite sector will continue to evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for satellite services. Superbird C2, with its current capabilities and potential for future enhancements, is well-positioned to navigate these changes. However, staying ahead of the curve will require ongoing investment in technology and a proactive approach to addressing the challenges of space debris and orbital congestion